什么是缓存
一种常见的网络优化手段,减少重复请求
缓存:保存资源副本数据,并在下次请求中直接使用该副本数据
分类
- 强缓存
- 浏览器根据请求的响应头判断是否需要请求服务器,如果无该缓存或缓存过期,则请求服务器,否则直接使用缓存
- 协商缓存
- 服务器会更加请求头的信息判断资源是否更新,如果有更新,则返回最新资源,否则直接使用缓存
强缓存
浏览器会根据请求的响应头中的 Expires 和 Cache-Control 字段判断是否命中缓存
Expires
app.use('/', (req, res) => {
const { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
if (pathname === '/') {
const html = fs.readFileSync(
path.resolve(__dirname, './public/index.html')
);
res.end(html);
} else if (pathname === '/1.jpeg') {
const img = fs.readFileSync('./public/1.jpeg');
// 强缓存 expires
res.set('Expires', new Date('2024-07-10 11:15:00').toUTCString());
res.end(img);
} else {
res.end('404');
}
});
第一次请求,响应数据,状态码 200
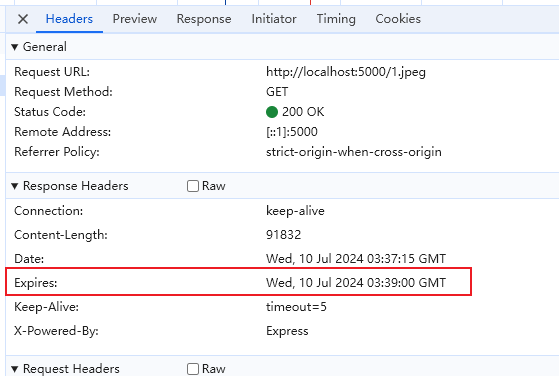
第二次请求,取缓存的数据
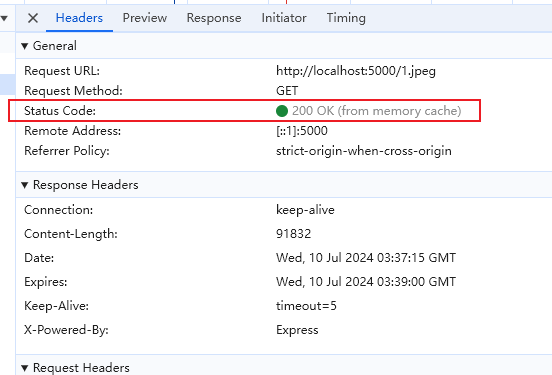
Expires 设置的是一个具体的时间,在该时间之前浏览器都会使用该缓存
:::tip 缺点:expires 时间依赖于客户端的时间,可能存在时间不准导致缓存过期 :::
Cache-Control
expires 是 http1.0 的参数,为了解决 expires 时间不准的问题,http1.1 引入了 Cache-Control,使用时长来判断缓存是否过期,但是 http1.1 还是兼容 expires 参数的
app.use('/', (req, res) => {
const { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
if (pathname === '/') {
const html = fs.readFileSync(
path.resolve(__dirname, './public/index.html')
);
res.end(html);
} else if (pathname === '/1.jpeg') {
const img = fs.readFileSync('./public/1.jpeg');
// 强缓存 cache-control
res.set('Cache-Control', 'max-age=10');
res.end(img);
} else {
res.end('404');
}
});
第一次请求,响应数据,状态码 200
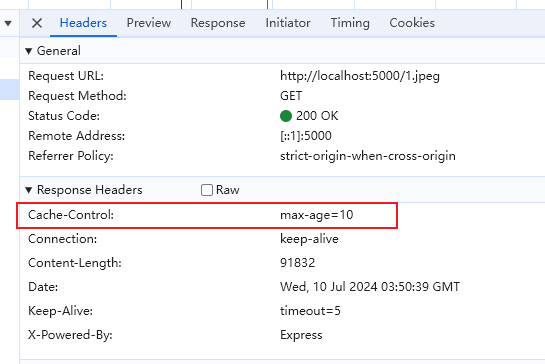
第二次请求,取缓存的数据
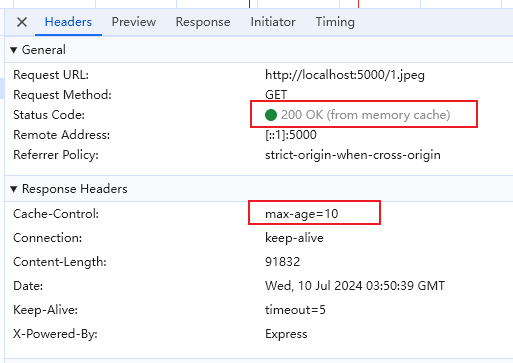
:::tip 如果同时存在 expires 和 Cache-Control,Cache-Control 优先级更高 :::
协商缓存
第一次请求,服务器会在响应头中添加 last-modified、etag 等字段,后续请求时浏览器会在请求头中用 If-Modified-Since、If-None-Match 带上 ast-modified、etag 字段的值,服务器会根据请求头中的 If-Modified-Since、If-None-Match 字段判断资源是否更新,如果有更新,则返回最新资源,否则直接使用缓存
last-modified/If-Modified-Since
app.use('/', (req, res) => {
const { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
if (pathname === '/') {
const html = fs.readFileSync(
path.resolve(__dirname, './public/index.html')
);
res.end(html);
} else if (pathname === '/2.jpg') {
const ifModifiedSince = req.headers['if-modified-since'];
// 文件时上一次修改的时间
const { mtime } = fs.statSync('./public/2.jpg');
// 判断文件是否更新
if (ifModifiedSince === mtime.toUTCString()) {
res.statusCode = 304;
res.end();
return;
}
const img = fs.readFileSync('./public/2.jpg');
res.set('Cache-Control', 'no-cache');
res.set('last-modified', mtime.toUTCString());
res.end(img);
} else {
res.end('404');
}
});
第一次请求数据,服务器获取文件上一次更新的时间并在响应头 last-modified 字段中返回给客户端,状态码 200
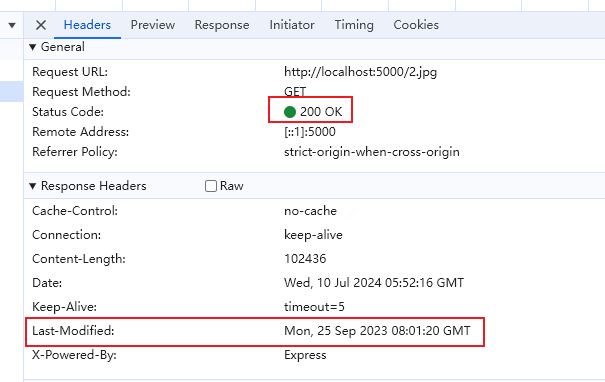
第二次请求数据,客户端在 If-Modified-Since 字段中带上上一次请求的 last-modified 的值,服务器判断两个值是否相同,如果相同,则返回 304 状态码,否则返回最新资源,状态码 200
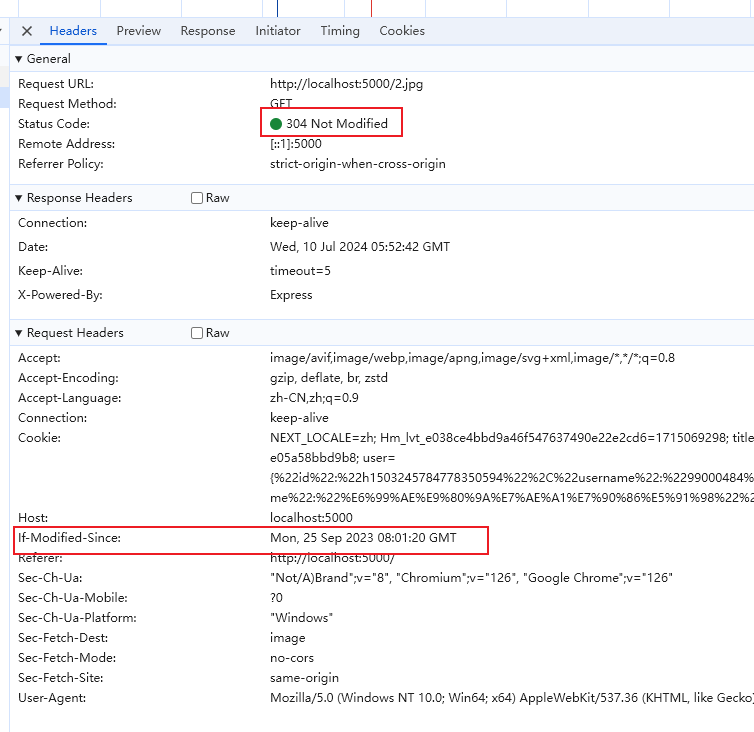
:::tip缺点:
- 如果资源更新,但内容并没有变化(先删除,再放进来),更新时间也会变化,造成网络资源的浪费
- last-modified 时间只能精确到秒,如果在 1 秒内多次修改文件,客户端可能没办法获取到最新的资源 :::
Etag/If-None-Match
app.use('/', (req, res) => {
const { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
if (pathname === '/') {
const html = fs.readFileSync(
path.resolve(__dirname, './public/index.html')
);
res.end(html);
} else if (pathname === '/2.jpg') {
const ifNoneMatch = req.headers['if-none-match'];
const img = fs.readFileSync('./public/2.jpg');
const hash = etag(img);
// 判断文件是否更新
if (ifNoneMatch === hash) {
res.statusCode = 304;
res.end();
return;
}
res.set('Cache-Control', 'no-cache');
res.set('Etag', hash);
res.end(img);
} else {
res.end('404');
}
});
第一次请求数据,服务器获取文件内容的 hash 值并在响应头 Etag 字段中返回给客户端,状态码 200
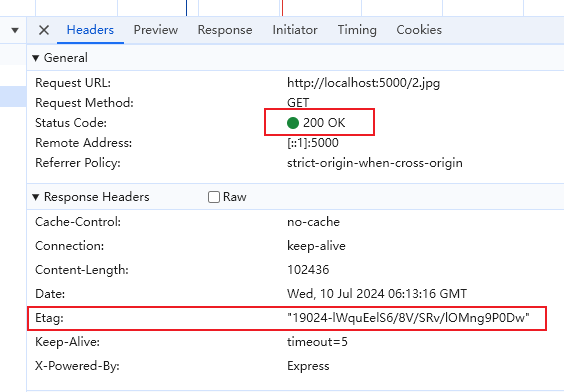
第二次请求数据,客户端在请求头 If-None-Match 字段中带上上一次请求的 Etag 的值,服务器判断两个值是否相同,如果相同,则返回 304 状态码,否则返回最新资源,状态码 200
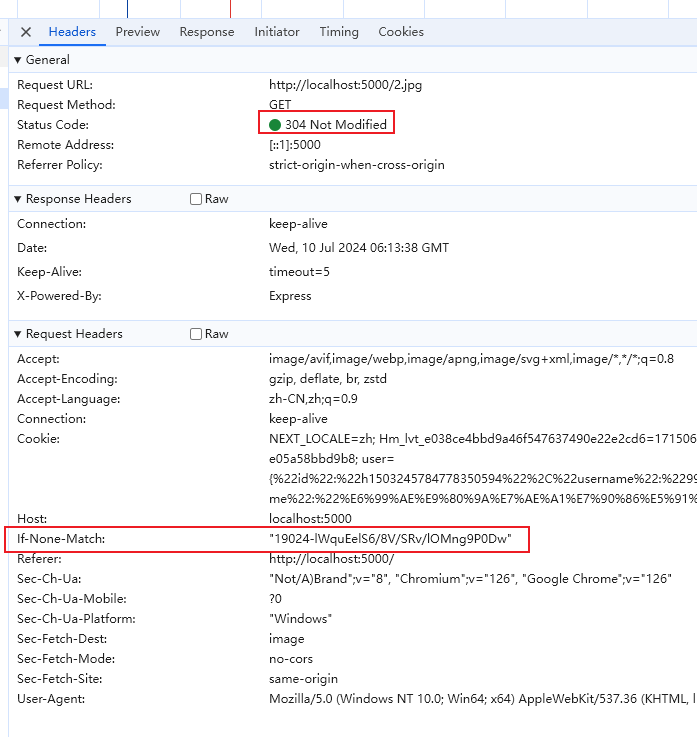
总结
- 强缓存优先级高于协商缓存,如果命中强缓存直接使用缓存
- Cache-Control 优先级高于 Expires
- Etag/If-None-Match 优先级高于 Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since
- Etag 精准度高于 Last-Modified,但生成 hash 需要不小的内存开销,性能比 Last-Modified 差
- 协商缓存并不会减少网络请求次数
- 一般网站部署时,html 文件使用协商缓存,js、css 等不经常变化的静态资源使用强缓存